
Transient global amnesia
Transient global amnesia (TGA) is a sudden memory loss condition, usually resolving within...

Orthostatic hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension, a drop in blood pressure upon standing, can result from various c...

Postural tachycardia syndrome
Postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS) is characterized by an excessive increase in heart ra...
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
This article provides a comprehensive overview of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), a d...

Primary Lateral Sclerosis
Primary Lateral Sclerosis (PLS) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by a slower p...

Spinal Muscular Atrophy
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is a genetic disorder characterized by the progressive weake...

Spinobulbar muscular atrophy
Spinobulbar muscular atrophy (Kennedy disease [KD]) is an X-linked disorder, typically man...

Brachial plexitis
Brachial plexitis, which can be acute or gradual in onset, typically presents with shoulde...

Bell's palsy
Bell's palsy, the most common cause of acute spontaneous peripheral facial paralysis, is b...
Polyneuropathy
The article discusses various types of immune-related neuropathies. It begins with an over...

Infectious neuropathy
The article outlines different neuropathic syndromes related to HIV and other infectious d...
Guillain Barré syndrome
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is characterized by progressive muscle weakness and diminish...
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathy encompasses various immune-mediated neuropathies, including Guillain-Barré...
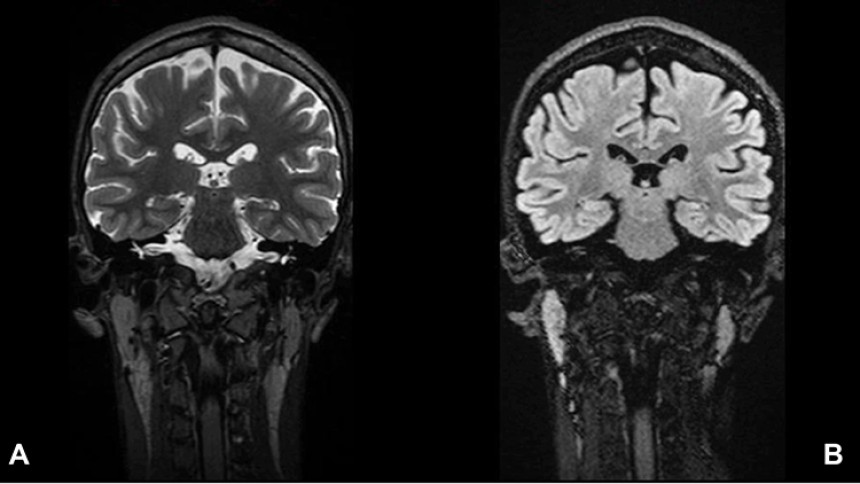
Miller Fisher syndrome
Miller Fisher syndrome, characterized by ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, and areflexia, often inv...
Multifocal motor neuropathy
Multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN) is a rare, slowly progressive disease characterized by a...

Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy encompasses polyneuropathy, radiculopathy, and mononeuropathy, often...
Vasculitic neuropathies
Vasculitic neuropathies, part of systemic vasculitis affecting various organs, present wit...
Multiple sclerosis Basic Management
Multiple Sclerosis, an immune-mediated CNS disease, has no cure but treatments delay progr...
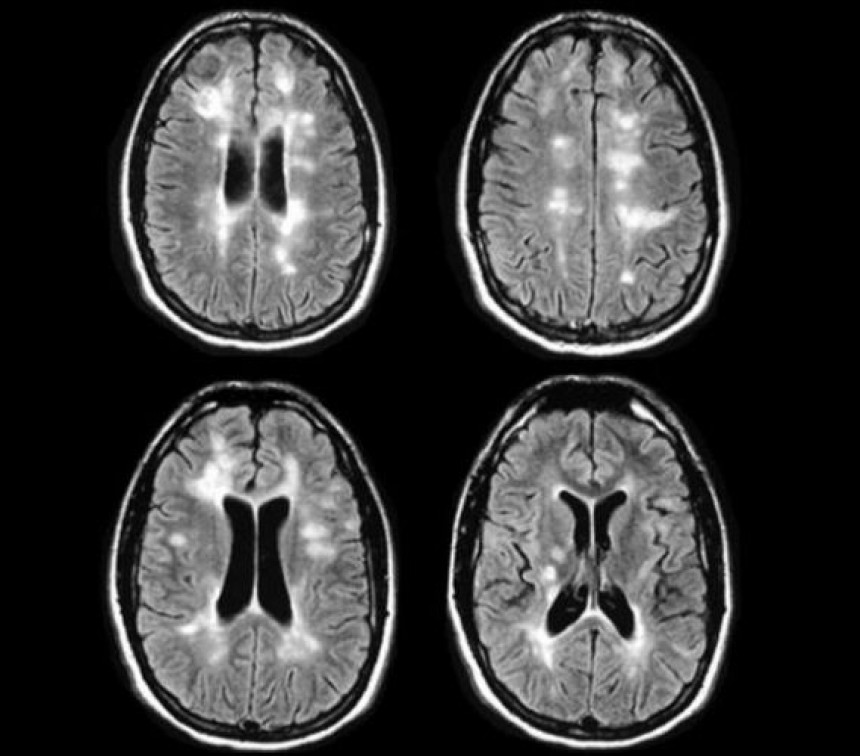
Multiple sclerosis RRMS Latest Diagnostic criteria
Relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) is diagnosed clinically, typically presenting in young adult...
Multiple sclerosis RRMS Choice of Initial Disease modifying Drugs
Disease Modifying Therapies (DMT) for Relapsing Remitting MS (RRMS) include oral agents (d...
Multiple sclerosis RRMS Role of antibodies and MRIs for monitoring
Monitoring the response to Disease Modifying Therapies in Relapsing Remitting MS involves...

Multiple sclerosis RRMS When to change disease modifying therapy
Changing Disease Modifying Therapy (DMT) in RRMS is considered for poor response, adherenc...

Multiple_sclerosis_PPMS_Criteria
Primary Progressive MS (PPMS) constitutes about 10% of MS cases and is characterized by a...

Multiple sclerosis SPMS Management
For Secondary Progressive MS (SPMS), active disease management involves switching to treat...

Multiple sclerosis Avonex protocol and monitorin
Interferon beta-1a is administered intramuscularly weekly for MS, starting with a quarter...

Multiple sclerosis Betaseron protocol and monitoring
Interferon beta-1b for MS is given subcutaneously every other day, with dose titration. Co...
Thalamic Pain Syndrome
Thalamic Pain Syndrome, often post-stroke, manifests with delayed neuropathic pain, temper...
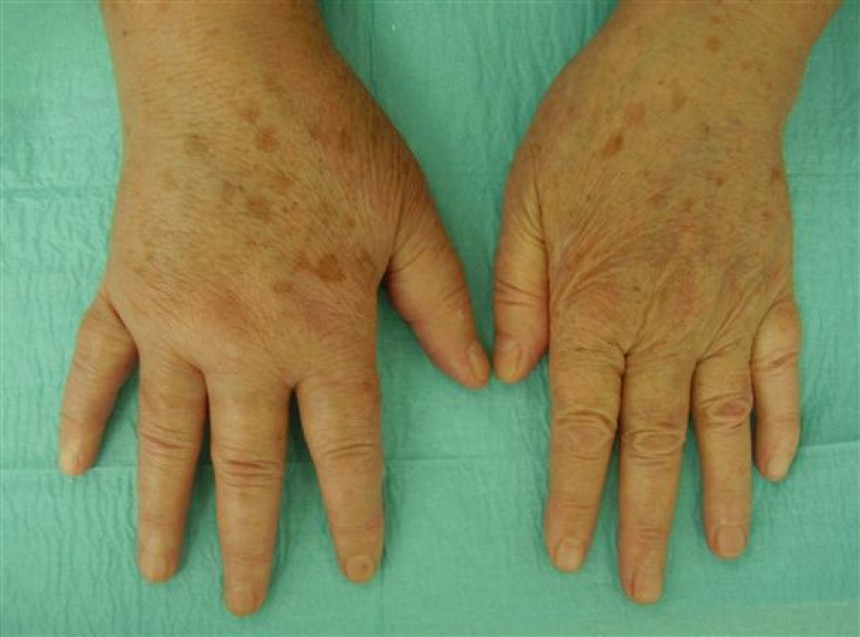
Complex regional pain syndrome - 1
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS), often post-injury, involves sensory, autonomic, and...

Complex regional pain syndrome - 2
CRPS Type II, following nerve injury, often affects upper limbs, causing burning pain and...

Multiple sclerosis Ocrevus protocol and monitoring
Ocrelizumab, used for B cell depletion, has risks of infusion reactions, infections, and l...